Unify data for
Get your data ready for AI with data unification and management. Deliver value for your business fast.
Trusted by 38 of the Fortune 500.
Stop choosing between speed and
quality—demand both.
Use well-governed, high-quality data in real time for unparalleled business responsiveness.
Immediate operational efficiencies.
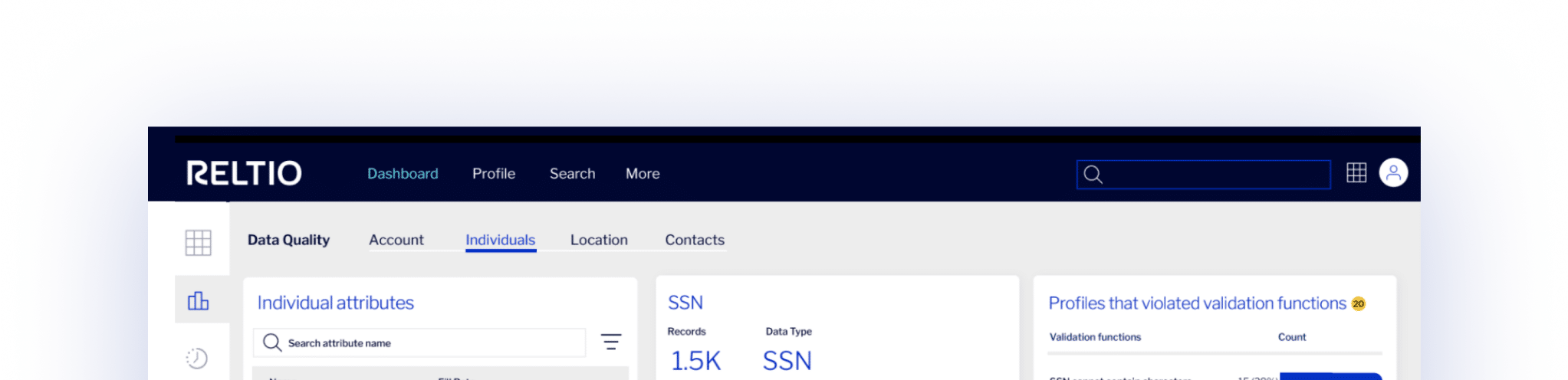
- Our customers have improved data stewardship productivity and reduced errors in manual data entry—saving $3.1M.
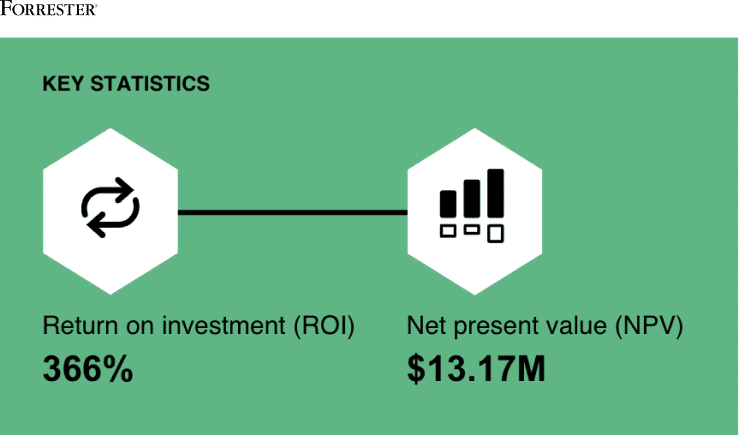
- Based on interviews with Reltio customers, Forrester Consulting shows a customer payback period of less than 6 months for a composite organization.
- Empire Life has achieved 60% increase in first-call reduction and lowered TCO by $1M from migrating from legacy MDM to Reltio.
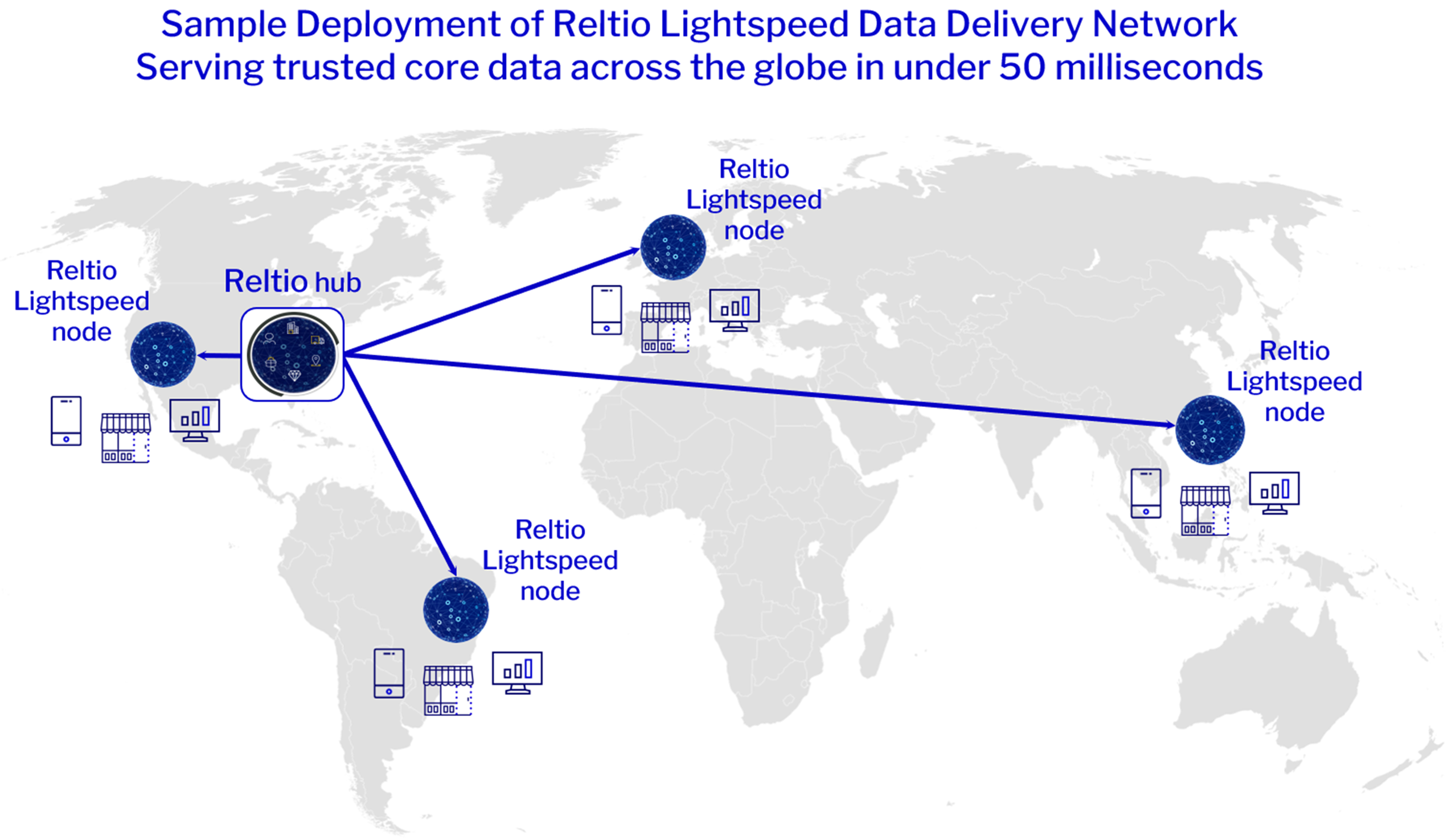
Instant, high-quality data for seamless experiences—anywhere.
Power global, real-time apps and analytics with Reltio Lightspeed Data Delivery Network to serve data in <50 ms at every point of engagement. Add Reltio Business Critical Edition for always-on 99.99% availability.
Value in weeks, not months.
Part of our platform, velocity packs include industry-and domain-specific data models and prebuilt components out of the box, which you can tailor as needed. So you can deliver cleansed, interoperable core data and business value in 90 days.
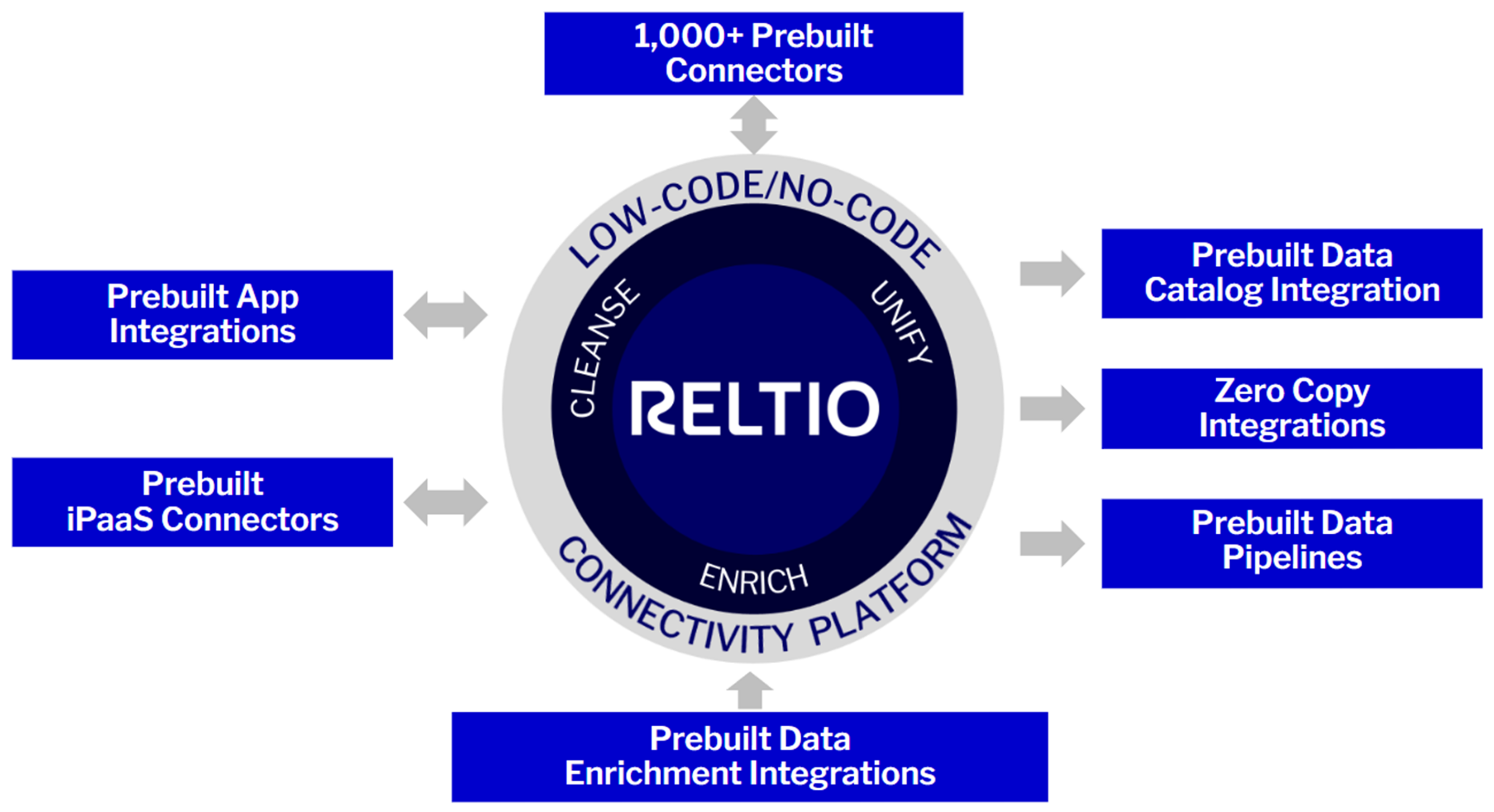
Open ecosystem for best-of-breed approach.
Easily tap into our partner ecosystem with our prebuilt integrations, data pipelines, and no-code/low-code development. Integrate popular data catalogs, data warehouses, analytics platforms, and much more.





61.1B
Total API calls
per year
9.1B
Consolidated profiles
under management
100B
Relationships under
management
140+
Countries with
Reltio users
Pioneering with genAI-driven innovation.
Ground-breaking gen AI and LLMs for data stewards.
Unprecedented speed. Unlimited potential.
Unified data using the newest artificial intelligence tech—generative AI, LLMs, and more.
LLM-driven match and merge.
Pretrained, secure ML models for automatic matching and merging. Powered by patent-pending Flexible Entity Resolution Networks that incorporate zero-shot learning.
Blazing fast data delivery network—globally.
Industry-first Reltio Lightspeed Data Delivery Network™ serves API-ready data anywhere in under 50 milliseconds.
Enhanced productivity with Reltio Intelligent Assistant (RIA).
Chat-based data exploration and documentation search. Powered by generative AI.
“The benefits have been incredible. We are now talking directly to millions of our consumers on a day-to-day basis. In 2023, we’ve sent about 1 billion personalized communications.”
Welington Fonseca, EVP Global Customer Marketing and eCommerce


Continuous innovation.
Immediate value.
Your organization’s reliance on trusted data is growing exponentially. You need innovation that keeps up with your business.
Our genAI-powered, business-responsive SaaS platform unifies and cleanses core data—delivering it in milliseconds wherever it’s needed. Deploy quickly and gain value in just 90 days.


Turn data into a
competitive advantage
As leaders in data management execution, technology, and project implementation, our service partners can help you accelerate value from your data, and deploy Reltio for your success. Made up of leading expert systems integrators, technology vendors, and data providers, consultants and implementation specialists, our partner-experienced network can ease implementation and accelerate impact.

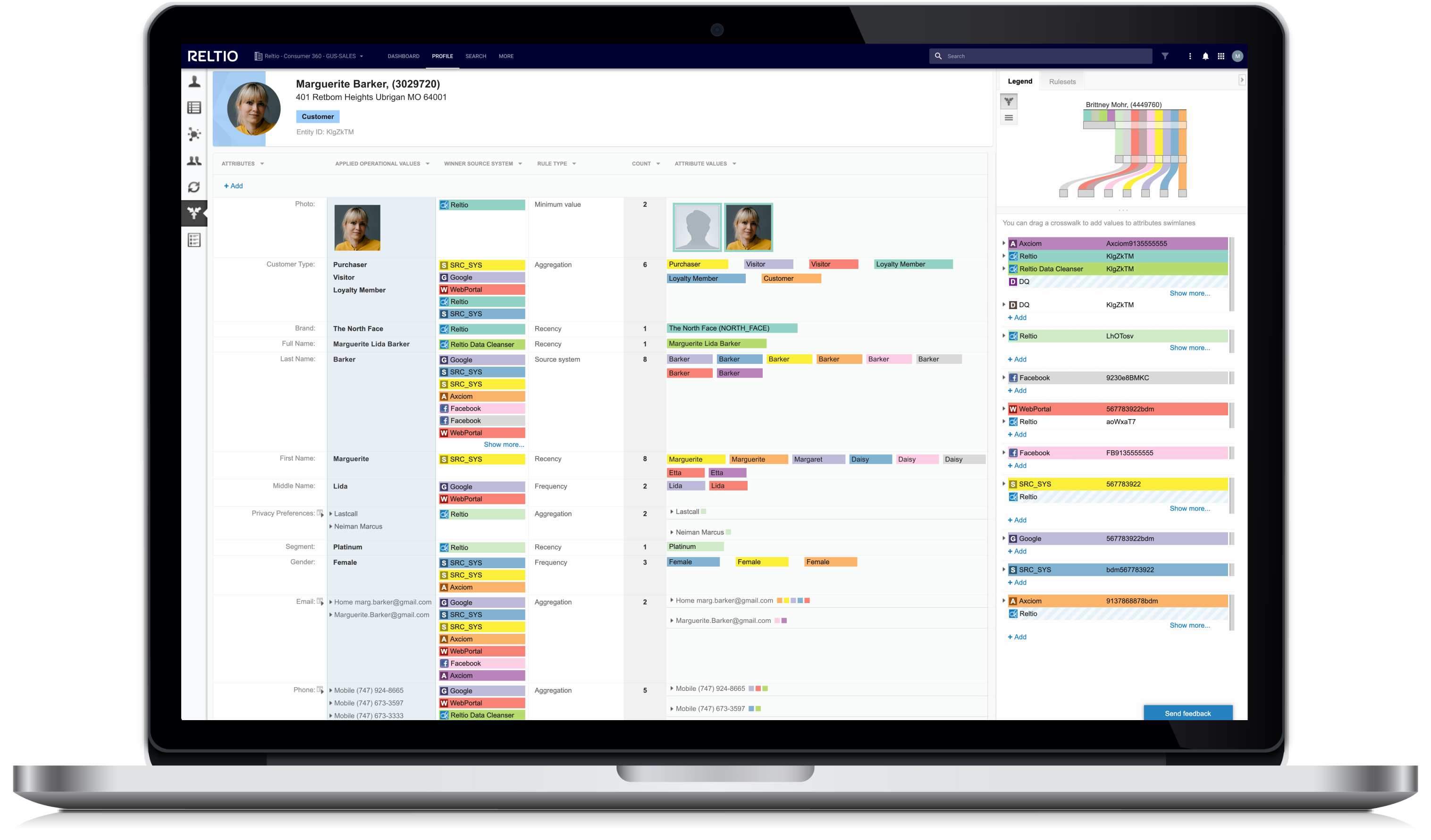
What makes Reltio Data Cloud different?
Real-time, ready-to-consume 360 views made easy.
- Move from one-off data projects to managing data assets as products.
- Stay ahead of business demands with reusable, trusted data using patent-pending, LLM-based Flexible Entity Resolution Networks (FERN).
- Use comprehensive profiles with interactions and derived attributes from enterprise sources for individuals and organizations.
- Mobilize interoperable customer data in milliseconds—and at scale.
Fuel your business with unified, trusted core data in real time.
- Turn siloed core data into your secure, best source of truth using our AI-powered automation.
- Get up and running in just 90 days with our industry- and domain-specific velocity packs.
- Plug into any data source and accelerate time to value with prebuilt connectors/integrations.
- Simplify data governance and privacy compliance with consent management, data masking, data lineage, and data catalog integration.
More ways to make more
of your data.
Ready to see it in action?
Get a personalized demo tailored to your
specific interests.